Not getting 12 volts to coil
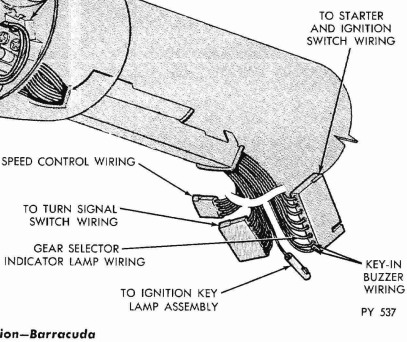
1970 Barracuda column connectors
Connector diagram
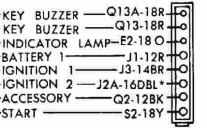
Battery 1, J1-12R is a 12 ga red wire that connects to the main splice. It gets power from the battery or alternator, whichever has higher voltage.
Accessory, Q2-12BK is a 12 ga black wire that provides power to many of the 'accessories' that gets power when the key is on or in accessory.
Ignition, J2A-16DBL* is 16 gage dark blue wire with white stripe for running the essential engine electrical items.
Bulkhead connectors on engine compartment side.
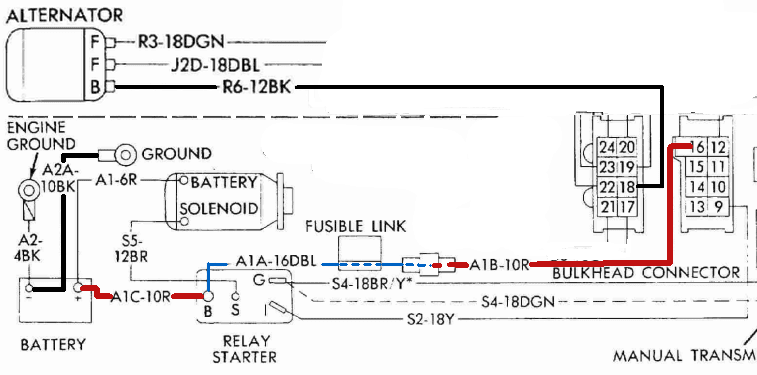
Battery (A1) goes to cavity 16
Alternator output (R6) goes to cavity 18.
We can add those details to the schematic.
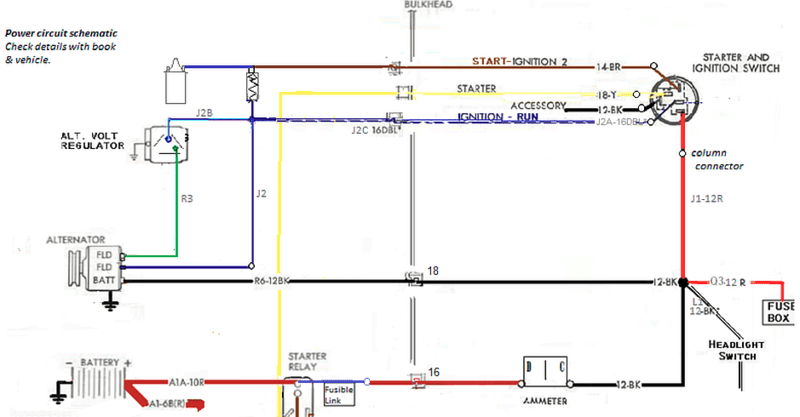
Now here's a couple of exampls of how to look for resistance.
(example 1) Engine Off, Key Off, Turn on parking lights:
About 4 amps of current flows from the battery to the lights and back to the battery. Path of current shown with orange arrows.
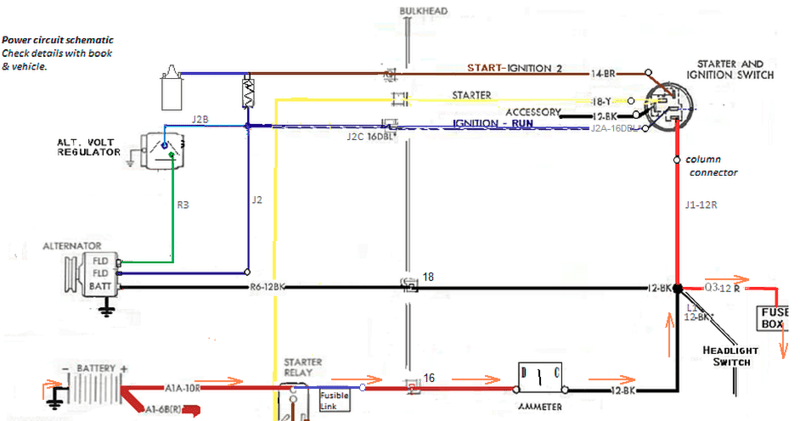
If there is resistance to the current between the battery positive and the main splice it will show up as a voltage drop.
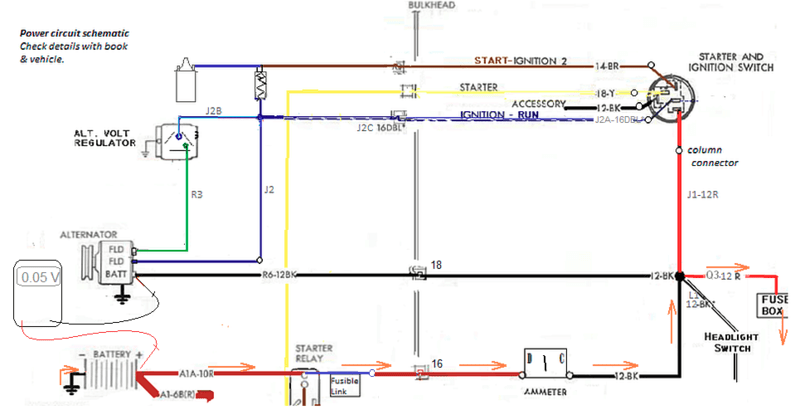
Turning on the headlights will increase the current to roughly 12 amps. This will result in more voltage drop through the resistance.
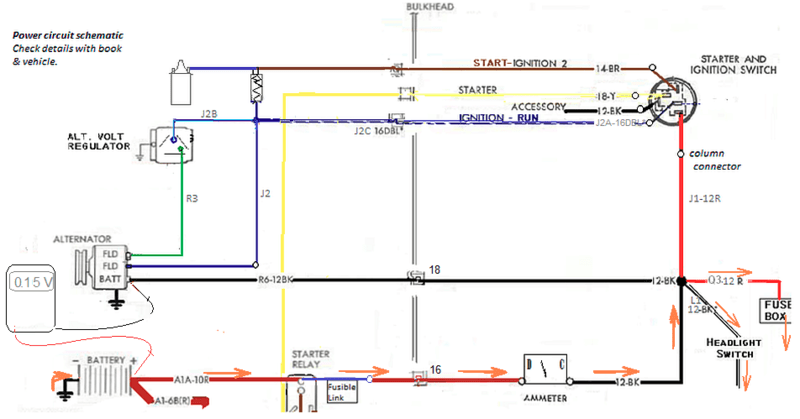
.15 V drop for 15 amps isn't bad.
(example 2). Engine running, battery fully charged, turn on headlights.
step 1. Start engine and allow battery to recharge. Ammeter must be at zero. Measure voltage to ground from Alt output. It should be around 14 Volts.
step 2. Measure voltage difference between alt out and battery. Turn on headlights. Measuer voltage drop with lights on.
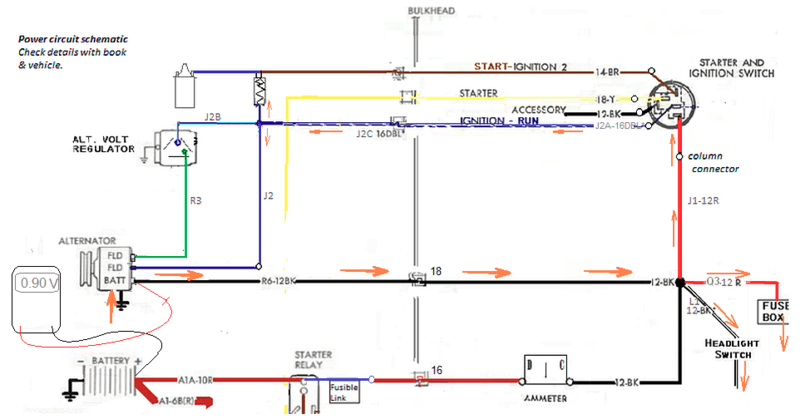
The voltage difference in this example indicates a fair amount of resistance in the the R6 line, probably at the connectors but could be damaged wiring.
1970 Barracuda column connectors
Connector diagram
Battery 1, J1-12R is a 12 ga red wire that connects to the main splice. It gets power from the battery or alternator, whichever has higher voltage.
Accessory, Q2-12BK is a 12 ga black wire that provides power to many of the 'accessories' that gets power when the key is on or in accessory.
Ignition, J2A-16DBL* is 16 gage dark blue wire with white stripe for running the essential engine electrical items.
Bulkhead connectors on engine compartment side.
Battery (A1) goes to cavity 16
Alternator output (R6) goes to cavity 18.
We can add those details to the schematic.
Now here's a couple of exampls of how to look for resistance.
(example 1) Engine Off, Key Off, Turn on parking lights:
About 4 amps of current flows from the battery to the lights and back to the battery. Path of current shown with orange arrows.
If there is resistance to the current between the battery positive and the main splice it will show up as a voltage drop.
Turning on the headlights will increase the current to roughly 12 amps. This will result in more voltage drop through the resistance.
.15 V drop for 15 amps isn't bad.
(example 2). Engine running, battery fully charged, turn on headlights.
step 1. Start engine and allow battery to recharge. Ammeter must be at zero. Measure voltage to ground from Alt output. It should be around 14 Volts.
step 2. Measure voltage difference between alt out and battery. Turn on headlights. Measuer voltage drop with lights on.
The voltage difference in this example indicates a fair amount of resistance in the the R6 line, probably at the connectors but could be damaged wiring.